How Long Does TMS Last?
Before and After TMS Therapy
Before TMS Therapy
Prior to initiating TMS sessions, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine suitability for the treatment. This includes a review of medical history, current medications, and mental health assessments. Patients are advised to remove any metallic accessories and remain relaxed during the procedure.
After TMS Therapy
Post-TMS sessions, most individuals can resume their daily activities immediately, as the procedure is non-invasive and doesn’t require anesthesia. Some patients might experience mild TMS after effects such as headaches or scalp discomfort, which typically diminish over time.
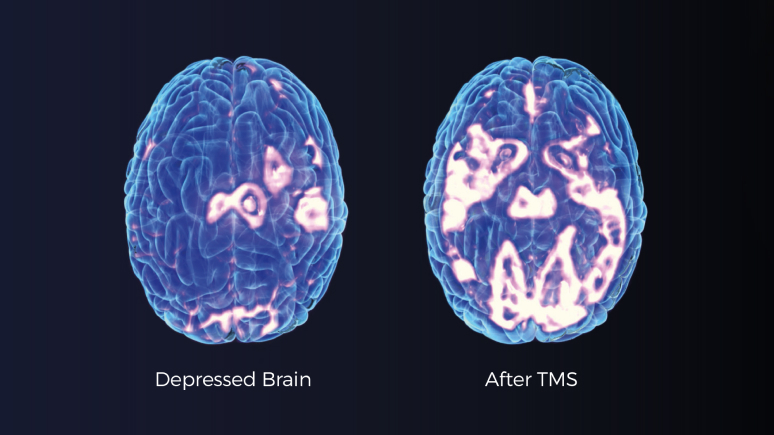
Following a course of TMS therapy, many patients report noticeable improvements in mood, energy levels, and overall functioning. The brain before and after TMS therapy shows changes in neural activity, particularly in areas involved in mood regulation. These alterations may contribute to the alleviation of depressive symptoms and improvement in overall mental health.
TMS vs. ECT: Differences and Effectiveness
When exploring advanced treatments for depression, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) are two prominent options. Both are FDA-approved and have demonstrated efficacy in managing treatment-resistant depression. However, they differ significantly in their methodologies, side effect profiles, and patient experiences.
Mechanism of Action
- TMS: Utilizes magnetic fields to non-invasively stimulate specific regions of the brain, particularly the prefrontal cortex, which is associated with mood regulation. This stimulation aims to enhance neural activity and alleviate depressive symptoms.
- ECT: Involves the application of controlled electrical currents to the brain under general anesthesia, inducing brief seizures. This process is believed to cause changes in brain chemistry that can rapidly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions
Procedure and Patient Experience
- TMS: Sessions are conducted on an outpatient basis, with patients remaining awake and alert. Each session typically lasts between 20 to 30 minutes, and no anesthesia is required. Patients can resume normal activities immediately post-treatment.
- ECT: Administered in a hospital setting, ECT requires general anesthesia and muscle relaxants. The procedure involves a recovery period, and patients may need assistance post-treatment due to temporary cognitive effects.
Side Effects
- TMS: Generally well-tolerated, with the most common side effects being mild scalp discomfort or headaches, which usually diminish over time.
- ECT: While effective, ECT is associated with more pronounced side effects, including short-term memory loss, confusion, and physical side effects related to anesthesia.
Effectiveness
- TMS: Studies indicate that TMS can lead to significant improvement in depressive symptoms, especially in individuals who have not responded to traditional treatments.
- ECT: Often considered when rapid response is necessary, ECT has a high efficacy rate, particularly in severe cases of depression, but the potential for cognitive side effects must be considered.
At Mind Your Mind NJ, we specialize in TMS therapy, offering a non-invasive and effective option for individuals battling depression. Our dedicated team is committed to providing personalized care to help you achieve optimal mental health.
Please contact us for more information or fill out the form below to request an appointment.